S13
S13 is composed of 3 alpha helices to form one globular domain.
Most proteins also include long extensions, and in S13, these
take the form of extended carboxy- or amino- terminal helices.
These tails are important for contact with RNA. They probably help
to stabilize tertiary structure as they can probe into the RNA,
approaching many RNA elements. Furthermore, S13 interacts with multiple proteins, including S3, S4,
S5, S7, S8, S9, S11, S12, S17, S19, and S21.
(Wimberly, 2000)
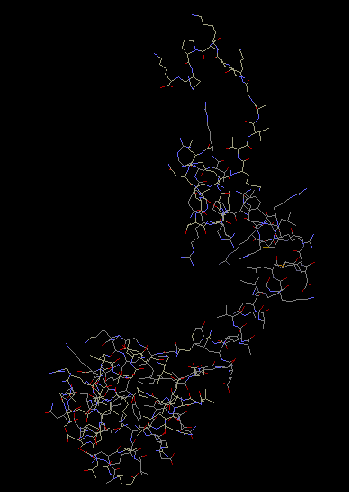
S16
Ribosomal protein S16 consists of two alpha helices and five beta strands
that are arranged in an antiparallel/parallel sheet. Its nearest protein neighbors
are S4 and S20. After these primary binding proteins bind to the 16S rRNA, S16 can
take its place in a crevice near helix 21. The binding of S16 causes a conformational
change in the ribosome, bringing it one step closer to its final shape.
(Allard, 2000)
(Stern, 1988)
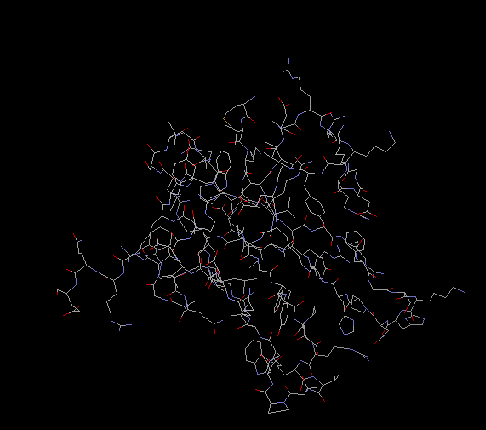
S18
The S18 protein consists of four alpha helices and is surrounded by an ordered
polypeptide coil. It becomes involved in the assembly of the growing ribosome after
S15 has bound to the rRNA. It cooperatively binds to S6 along its beta sheet and
makes contact to the RNA backbone in the upper three helix junction of helices 20,21,
and 22. It interactions with S6 are characterized by van der waals forces and salt bridge
interactions. It is proposed that S18 can only fold once it is bound to S6 to make a
heterodimer. S18 also interacts with S14, S11, and S21.
(Agalarov, 2000)
(Wimberly, 2000)
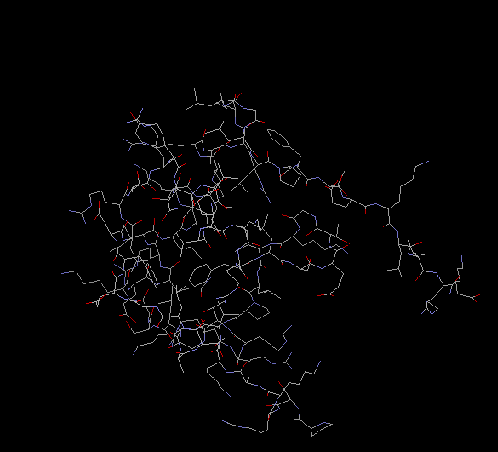
S19
S19 contains 93 amino acids and is a 10.6 kDa protein. While it does bind
to the 3' major domain of the 16s rRNA, it can not bind unless S7 has already done
so, creating the S19-binding site. It is located close to S14 and forms a protein
pair with S13. S19's secondary structure consists of an alpha helix and three B strands
in a parallel/antiparallel pattern. The protein has long disordered tails which are
important for interactions with other ribosomal proteins.
(Helgstrand, 1999)
Return to all proteins
Return to index



