Overview
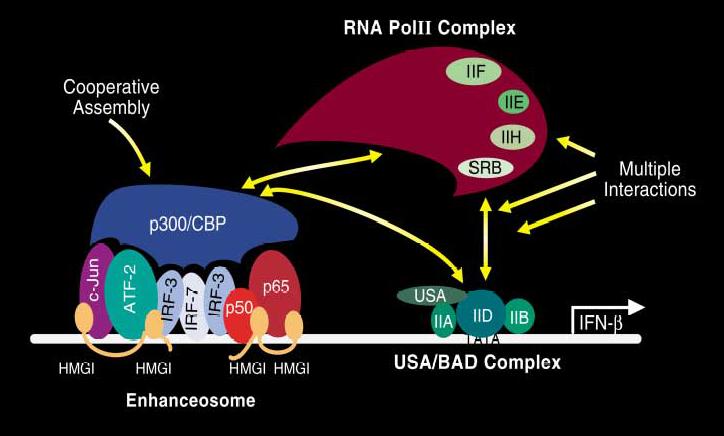
(Source: Maniatis, T. et. al. (1998),
Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol., 63, p.613)
Transcription of the INF-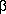 is
initiated as a result of viral infection via a well-defined and
ordered series of steps. Formation of the enhaceosome complex is
the key to control of transcription in response to environmental cues.
Control of transcription is achieved via concerted
combinatorial and synergistic
action of activators, as depicted in the above figure.
Viral-induced expression of Interferon is believed to occur via the following
ordered steps:
is
initiated as a result of viral infection via a well-defined and
ordered series of steps. Formation of the enhaceosome complex is
the key to control of transcription in response to environmental cues.
Control of transcription is achieved via concerted
combinatorial and synergistic
action of activators, as depicted in the above figure.
Viral-induced expression of Interferon is believed to occur via the following
ordered steps:
Within four hours of viral infection, several activators bind to a
65 base-pair long, nucleosome-free "enhancer" region of chromatin,
upstream of the core promoter.
NF- B and IRF-1 bind first, followed by
ATF-2, IRF-3 and c-Jun, and finally IRF-7. The binding of these species
occurs cooperatively with the HMG-I(Y) architectural factor.
B and IRF-1 bind first, followed by
ATF-2, IRF-3 and c-Jun, and finally IRF-7. The binding of these species
occurs cooperatively with the HMG-I(Y) architectural factor.
The assembled nucloprotein complex subsequently recruits Gcn5 histone
acetylase, which acetylates histones in the neighboring nucleosome, as
well as the Lys-71 residue of the HMG-I(Y), thereby stabilizng the enhanceosome
complex. The stable enhanceosome then recruits the CREB binding protein (CPB),
and the RNA Pol II complex. This is followed by recruitment of the SWI/SNF
complex, which remodels the chromatin by loosening the nucleosome
over the core promoter region, allowing the TFIID transcription factor access
to the gene, and switching on transcription.
Eventually, CPB acetylates the Lys-65 residue of the HMG-I(Y), disrupting the
enhanceosome, and terminating transcription.
Refrences:
- Struhl, K., A Paradigm for Precision, Science, 293, pp.
1054-1055 (2001)
- Carey, M., The Enhanceosome and Transcriptional Synergy, Cell, 92,
pp.5-8 (1998)
- Maniatis, T. et. al., Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant.
Biol., 63, pp.609-620 (1998)
- Agalioti, T. et al., Ordered Recruitment of Chromatin
Modifying and General Transcription Factors to the IFN-beta promoter,
Cell, 103, pp.667-678 (2000)
- Yie, J. et al., Mechanism by which the IFN-beta Enhanceosome
Activates Transcription, PNAS, 96, pp.13108-13113 (1999)
Return to top-level Enhanceosome page
 is
initiated as a result of viral infection via a well-defined and
ordered series of steps. Formation of the enhaceosome complex is
the key to control of transcription in response to environmental cues.
Control of transcription is achieved via concerted
combinatorial and synergistic
action of activators, as depicted in the above figure.
Viral-induced expression of Interferon is believed to occur via the following
ordered steps:
is
initiated as a result of viral infection via a well-defined and
ordered series of steps. Formation of the enhaceosome complex is
the key to control of transcription in response to environmental cues.
Control of transcription is achieved via concerted
combinatorial and synergistic
action of activators, as depicted in the above figure.
Viral-induced expression of Interferon is believed to occur via the following
ordered steps:

 B and IRF-1 bind first, followed by
ATF-2, IRF-3 and c-Jun, and finally IRF-7. The binding of these species
occurs cooperatively with the HMG-I(Y) architectural factor.
B and IRF-1 bind first, followed by
ATF-2, IRF-3 and c-Jun, and finally IRF-7. The binding of these species
occurs cooperatively with the HMG-I(Y) architectural factor.