EUKARYOTIC RNA POLYMERASE II
By:T. Akinyemi, B.C. Ego-Osuala, C.S. Obidi, D.M. Smith, G. Tangham
RNA Polymerase II transcription initiation complex of
yeast( S. cerevisiae); Adopted from
http://www.mips.biochem.mpg.de/proj/yeast/pathways/young.html
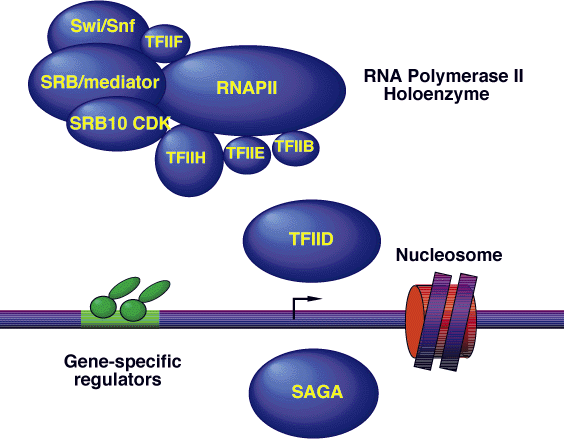
The links Below will take you through the discovery of RNA polymerase II
to
a description of the function and its 12 sub-units which all
interact to make the whole enzyme work
Brief Description
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes
Deoxy-ribonucleic Acid (DNA) into
RNA. This is done by the polymerase opening up the
Deoxy-ribonucleic Acid DNA where it
recognizes a promoter sequence. It begins transcription aproximately 10
bases
after the promoter sequence.